Hydraulic Power Unit | components | working principle
Hydraulic Power Unit
VisitCount 100
What Is a Hydraulic Power Unit (HPU)
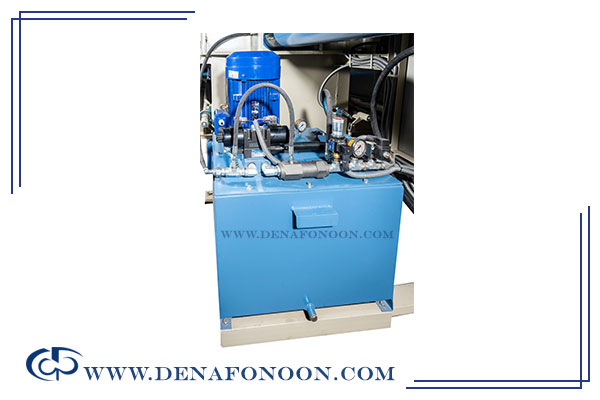

A Hydraulic Power Unit (HPU) is a power-generating system in which hydraulic fluid is used to perform mechanical work. These systems are commonly referred to by several names in the market, including:
- Power Pack
- Power Unit
- Hydraulic Power Module
HPUs are primarily used to deliver power through single-phase motors up to 2.2 kW, and three-phase motors up to 160 kW. If the power source is an electric motor, the selection is typically based on IEC standards, which define motor power ratings and dimensions, In other cases, sizing is determined by technical experts to match the power requirements of the system.
Main Components of a Hydraulic Power Unit
A hydraulic power unit consists of various key elements that work together to generate, control, and distribute hydraulic energy. These include:
Hydraulic Oil Tank
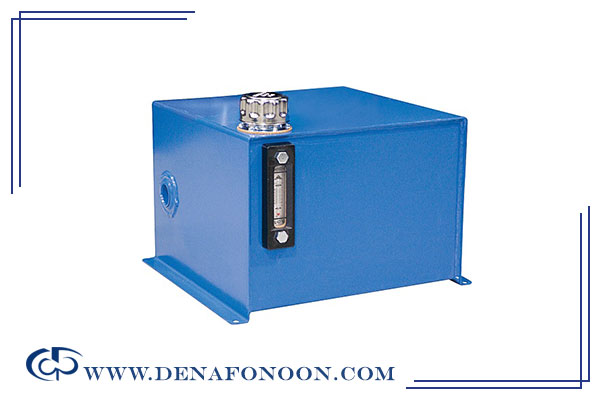

This reservoir holds hydraulic oil used to supply the pump and other components. The hydraulic fluid plays several roles:
- Transfers hydraulic power
- Lubricates moving parts
- Cools the system
- Helps maintain system cleanliness
The tank is usually designed to be up to 5 times the oil consumption, although layout and space considerations may influence its final size.
Electric Motor (Electromotor)
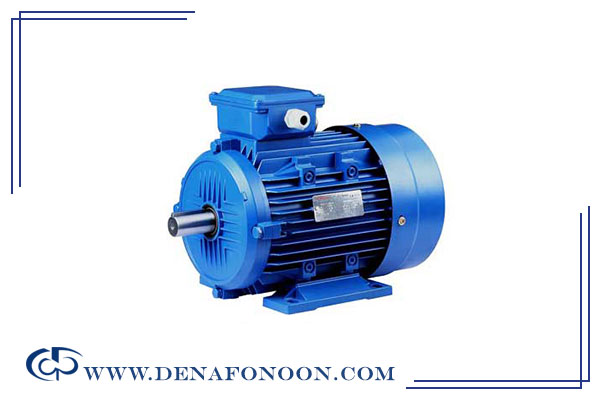

The electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy and drives the twin hydraulic pump. Important motor specifications include:
- Power rating (must match system pressure and pump capacity)
- Motor speed (RPM)
- Power source (single or three-phase)
- Motor type (induction, servo, etc.)
Pressure Control Valves
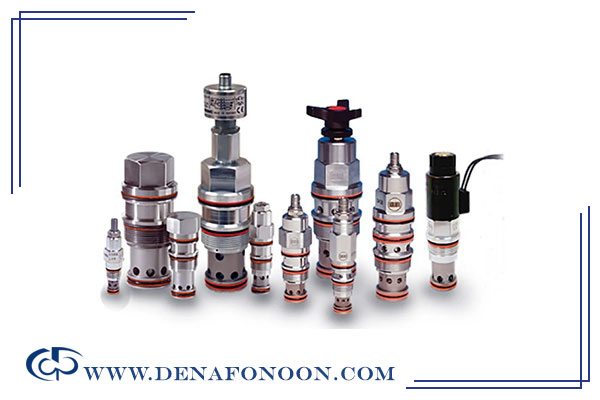

These valves regulate system pressure and are essential in almost every hydraulic system. Common types include
- Relief valves
- Pressure-reducing valves
- Counterbalance valves
- Unloading valves
- Sequence valves
All are used to ensure the pressure remains within safe and efficient operating limits.
Double Solenoid Directional Valve
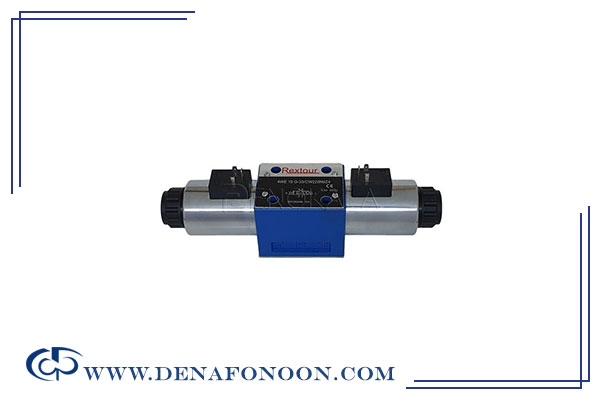

Also known as double-head solenoid valves, these control the direction of hydraulic fluid in the system, They function by energizing coils (solenoids) located on both ends of the valve, which redirect the fluid path. This enables precise control over actuator movement.
Check Valve (One-Way Valve)
.jpg)
Check valves allow fluid to flow in only one direction, preventing any backflow. This ensures unidirectional movement and protects the system from reverse pressure surges.
Flow Meter (Flow Rate Sensor)
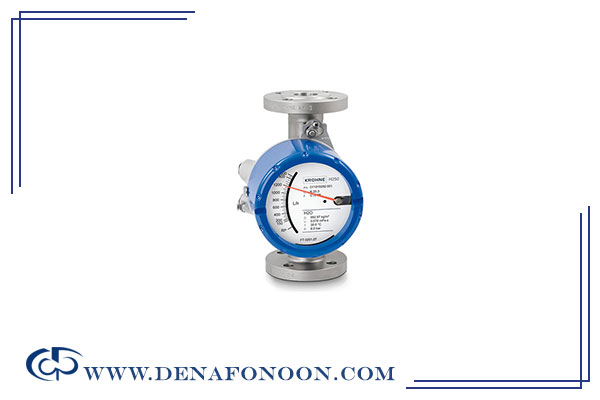

The flow meter, or flowmeter, measures the volume of fluid passing through a section per unit of time. Accurate measurement depends on:
- Fluid's chemical/physical properties
- Proper installation direction
- Environmental temperature changes
- Pipe material and condition
- Fluid corrosiveness
- Equipment application
Oil Filter
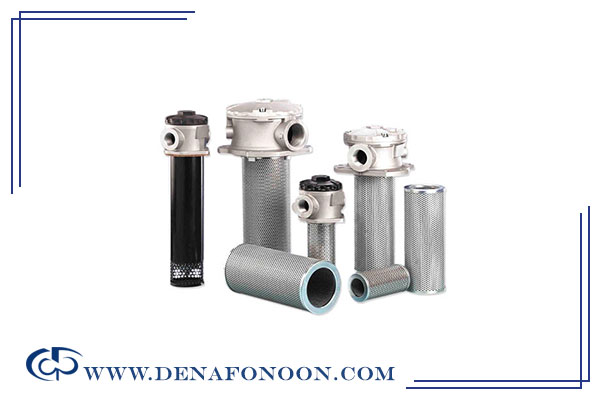

The oil filter is usually installed inside the hydraulic tank and serves to remove contaminants and purify the hydraulic fluid. Clean oil not only ensures efficient system performance but also extends the service life of components such as pumps, valves, and actuators.
Twin Hydraulic Pump
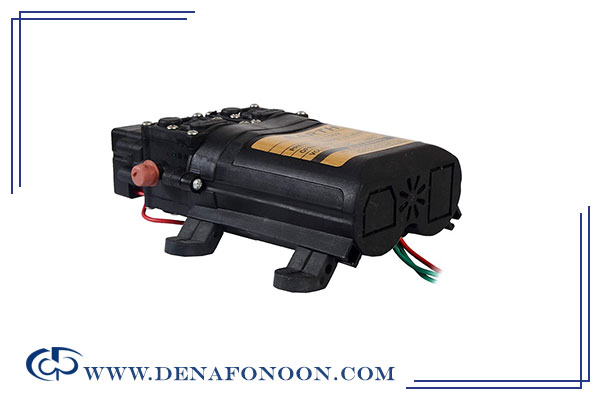

Often referred to as the heart of the HPU, the twin hydraulic pump is responsible for generating the necessary fluid flow and pressure. It converts mechanical energy from the motor into hydraulic energy, pushing oil through the system to drive actuators like hydraulic cylinders or motors.