The Role of Water in Various Industries
The Role of Water in Various Industries
VisitCount 125
The Role of Water in Various Industries

Water is one of the most critical resources in industrial processes, playing diverse and essential roles. In some industries, such as food production and chemical manufacturing, water is directly used as a raw material. In contrast, in sectors like power plants or steel factories, it primarily serves as an auxiliary medium for cooling equipment.
Moreover, water is indispensable in processes such as:
- Cleaning production lines
- Generating steam for energy supply
- Wastewater treatment
The quality of water used directly affects system efficiency and the final product’s quality. For instance, high mineral content not only causes scaling and equipment damage but also increases maintenance costs and reduces product quality. In sensitive industries such as pharmaceuticals, using pure, contamination-free water is essential to comply with health standards.
Due to high consumption volumes, water resource management in industry is vital. Inefficient or unplanned use can put immense pressure on water sources, potentially halting production lines or significantly increasing costs. Therefore, optimizing water use and implementing precise management strategies are essential for sustainable industrial operations.
1. The Role of Water in the Stone Industry

- Cooling cutting blades and polishing heads during contact with stone
- Washing and transporting dust particles generated from cutting and polishing
- Preventing the spread of environmental dust caused by stone processing
2. The Role of Water in Sand and Gravel Mines

Sand and gravel mines, due to their specific climatic and geological conditions, generate wastewater containing significant amounts of mud and suspended solids. Since these particles vary in nature, each washing unit applies a specific treatment method based on wastewater analysis.
Experts at DenaFonoon Company evaluate the treatment methods, water treatment systems, and filter press solutions to provide customers with the most cost-effective and practical recommendations. Typically, the type, capacity, and arrangement of treatment equipment are tailored to each plant, resulting in different setups for different sites.
3. The Role of Water in Agriculture
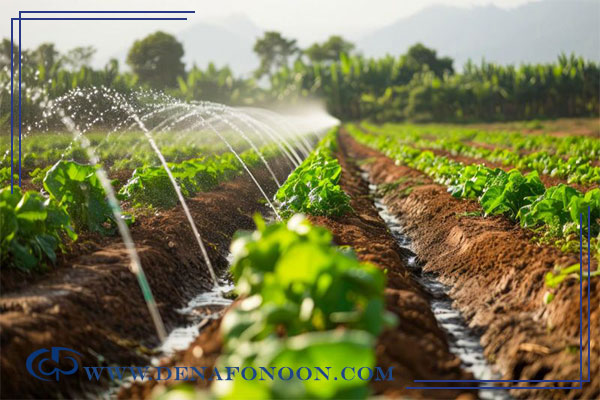

Agriculture accounts for the largest share of water consumption, with approximately 40% of farmland irrigated using groundwater. When high-efficiency irrigation systems are combined with proper water accounting and strict extraction regulations, water wastage in the basin can be reduced by more than 70%.
Wastewater management is also crucial. The safe reuse of treated wastewater in agriculture allows nutrient recovery and provides significant benefits for human health and the environment. Nutrient recovery from wastewater not only meets part of the global agricultural demand but also generates revenue and economic benefits. Globally, approximately **380 cubic kilometers of wastewater** are produced annually, which, after treatment, could irrigate millions of hectares of farmland.
4. The Role of Water in the Textile and Apparel Industry
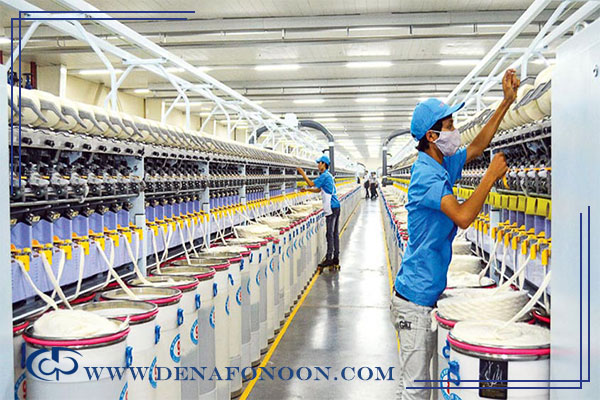

Water consumption in the textile industry is significant, especially during:
- Fiber washing
- Dyeing
- Printing
- Fabric finishing
On average, producing one kilogram of fabric requires 50 to 300 liters of water. Due to the high presence of organic and chemical pollutants, wastewater treatment is essential. Besides reducing environmental hazards and protecting ecosystems, treatment enables the reuse of water in processes such as equipment cleaning.
5. The Role of Water in Mining and Metallurgical Industries
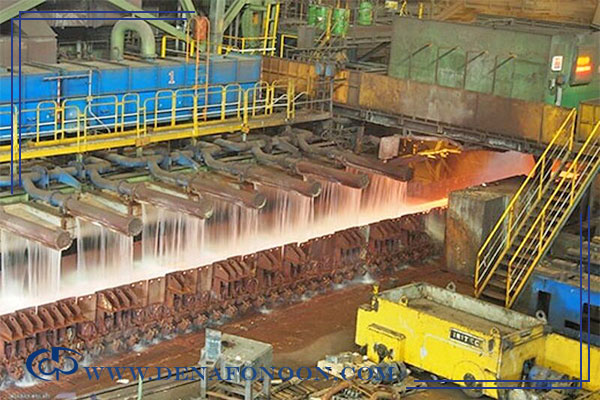

Water is consumed in two main stages: extraction of raw materials and processing/production, which leads to high water usage.
1.Key water-consuming processes in the mining industry include:
- Extraction and washing of minerals: washing and separating impurities from ores such as coal, iron, copper, and gold.
- Concentration and flotation: separating valuable particles from tailings, which consumes large amounts of water.
- Dust suppression: water spraying is essential, especially in open-pit mines, to control dust spread.
2.Water-intensive metallurgical industries include:
- Steel and Ironmaking: cooling furnaces, equipment, and steel products; producing steam for toxic gas scrubbing.
- Copper, Aluminum, and Non-Ferrous Metals: refining and smelting processes require water for cooling and electrochemical processes. In aluminum production, water is crucial for electrolysis and electrode cooling.
- Cement and Gypsum Industries: water is used for grinding raw materials, clinker production, and cooling equipment.
3.trategies to optimize water use include:
- Recycling water in steel plants and mines
- Using dry processing technologies in mineral beneficiation
- Installing industrial wastewater treatment systems to reduce pollution
- Replacing part of freshwater use with treated municipal or industrial wastewater
6. The Role of Water in the Food and Beverage Industry
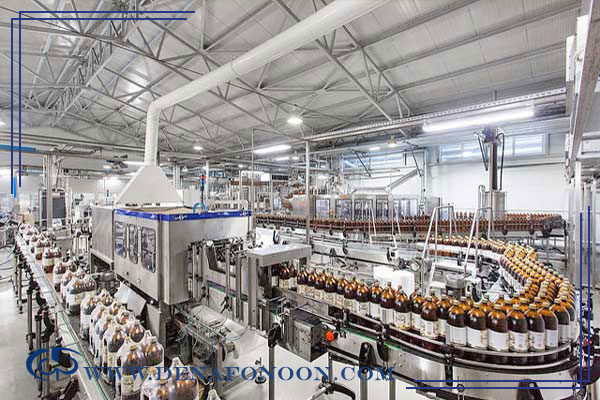

Water plays a crucial role in both the composition of food and beverages and in hygiene and sanitation. Key roles include:
- As a raw material: water is an essential component in the formulation and processing of products.
- Cleaning and hygiene: washing raw materials, production lines, equipment, and sterilization.
- Cooling and temperature control: maintaining proper process and storage temperatures.
- Quality control: water quality directly impacts the taste, safety, and shelf life of products.
- Treatment and recycling: treated wastewater can be safely reused in cleaning processes, reducing environmental impact.
In summary, water in the food industry serves three main functions:
- As a production raw material
- As a hygienic and process tool
- As a quality and safety control factor